Key Takeaways:
- Understanding the fundamentals of MPLS and its role in modern networking
- The benefits and limitations of MPLS compared to other technologies
- Future trends in network infrastructure and where MPLS fits
- Best practices for organizations looking to leverage MPLS
Introduction to MPLS
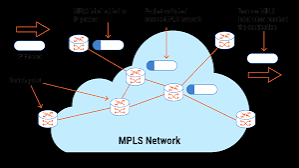
Multi-Protocol Label Switching (MPLS) is widely used to speed up network traffic flow and make it easier to manage. But what makes MPLS so valuable in today’s rapidly changing technological landscape? This networking strategy uses labels to route traffic efficiently, offering an alternative to traditional IP routing. Unlike conventional methods that rely solely on IP addresses, MPLS directs data from one node to the next based on short path labels rather than long network addresses, avoiding complex lookups in routing tables.
Designed to achieve high-speed data transfer and enhance overall network performance, MPLS has become a staple for many organizations. By understanding MPLS’s key concepts and applications, businesses can better prepare for future technological advancements. Furthermore, MPLS is known for its ability to support a variety of network protocols, making it an adaptable solution suitable for various industries, from telecommunications to finance.
The Advantages of MPLS
MPLS offers a multitude of benefits that contribute to its widespread adoption. Firstly, MPLS enhances quality of service (QoS) by prioritizing specific types of data traffic, such as VoIP calls or critical applications, thereby ensuring minimal latency and optimal performance. This prioritization allows for smoother operation of time-sensitive applications, contributing to better user experiences and operational efficiency. Additionally, MPLS provides more reliable and quicker failover capabilities, which are crucial for business continuity. In the event of a link failure, MPLS can reroute traffic almost instantaneously, minimizing downtime and potential revenue loss.
Another significant advantage is its scalability. MPLS can manage increasing amounts of data without compromising performance, making it a viable solution for growing businesses. As companies expand and their networking needs evolve, MPLS can quickly adapt to new demands, offering seamless integration with existing infrastructure. Enhanced traffic engineering also allows for optimized route selection, reducing congestion and improving network efficiency. Organizations can achieve better bandwidth utilization by leveraging these optimized routes, enhancing their network’s overall performance.
Comparing MPLS with Other Technologies
When considering network infrastructure options, it’s essential to weigh MPLS against alternatives such as Software-Defined Wide Area Networking (SD-WAN) and traditional WANs. While each has its advantages, MPLS stands out for its ability to provide consistent performance and reliability. Unlike conventional WANs that depend heavily on public internet connections, MPLS offers dedicated routes and circuits, ensuring more stable and secure connections.
SD-WAN, for instance, offers increased flexibility and cost savings through broadband internet connections. It allows companies to manage their networks through software, reducing reliance on physical hardware. However, it may not match MPLS’s performance and reliability levels in specific scenarios, such as real-time applications. On the other hand, traditional WANs are often limited by their reliance on public internet connections, leading to higher latency and vulnerability to attacks. Organizations must weigh these factors to determine which solution best meets their needs and goals.
Future Trends in Network Infrastructure
The field of network infrastructure is constantly evolving. One notable trend is integrating artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) for improved network management and security. These technologies can analyze traffic patterns and predict potential issues before they become critical, enabling proactive management and quicker resolution of network problems. AI-driven analytics also facilitate better decision-making, helping organizations optimize their network architectures for maximum efficiency.
Moreover, the growing adoption of SD-WAN signifies a shift towards more flexible and dynamic networking solutions. Organizations seek ways to combine the best features of MPLS and SD-WAN to achieve optimal results. Emerging trends such as virtualization and cloud-native technologies further influence network designs, pushing companies to adopt more agile and scalable solutions. The convergence of these trends is set to redefine the network infrastructure landscape, offering enhanced functionality and greater adaptability to changing business needs and technological advancements.
Best Practices for Implementing MPLS
If your organization considers adopting MPLS, following best practices can lead to a successful implementation. Start by selecting a reliable service provider with experience in MPLS deployments. They should offer comprehensive support and customization to meet your unique needs. Working with a knowledgeable provider can help smooth the transition and ensure your MPLS solution is tailored to your requirements, from initial setup to ongoing maintenance.
Another crucial step is to conduct a thorough network assessment. Understanding your current infrastructure and identifying areas that will benefit from MPLS is critical. This involves evaluating existing traffic patterns, potential bottlenecks, and security requirements. A comprehensive assessment helps design a solution that aligns with your organization’s operational objectives, optimizing performance and cost efficiency.
Additionally, planning for scalability is essential. Ensure that your MPLS solution can adapt to future growth and evolving business needs. Consider incorporating hybrid solutions that combine MPLS with other technologies, such as SD-WAN, to maximize flexibility and performance. Such hybrid approaches allow organizations to leverage both technologies’ strengths, providing a more resilient and adaptable network strategy. Employing these best practices ensures that the implementation is smooth and that the benefits of MPLS are fully realized, contributing to long-term success and competitive advantage.
Conclusion
MPLS remains a robust and reliable technology in network infrastructure. While other technologies are emerging, understanding where MPLS fits into the bigger picture will be crucial for businesses aiming to optimize their networks. The synergistic combination of MPLS with newer technologies like SD-WAN can provide the best of both worlds, ensuring an innovative and robust network strategy.
As businesses continue to evolve and expand, MPLS offers the stability and predictability necessary for mission-critical applications, making it a valuable component of a hybrid networking approach. By leveraging MPLS alongside modern solutions, companies can achieve enhanced performance, security, and scalability across their networks. This blend allows for greater flexibility in managing traffic flows and optimizing bandwidth, ensuring efficient and reliable communication between dispersed locations. Additionally, MPLS’s ability to prioritize traffic and provide consistent quality of service (QoS) remains a crucial advantage in today’s increasingly complex network environments. Ultimately, integrating MPLS with newer technologies positions businesses to meet current demands while future-proofing network infrastructure.